Cellular respiration is a biochemical process that provides energy to cells by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen. This complex process takes place in the mitochondria and is fundamental to the life of both plants and animals. Here, we’ll explore its outputs, reactants, main energy sources, and how it contributes to ATP production.
What Are the Products of Cellular Respiration?
The primary products of cellular respiration are:- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – This gas is released as a waste product during the Krebs cycle.
- Water (H₂O) – Formed when oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, combining with hydrogen ions to form water.
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) – This is the energy currency of the cell, generated throughout cellular respiration.
What Is an End Product of Cellular Respiration?
The ultimate end products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Of these, ATP is the most critical for cellular functions, fueling nearly all cellular processes.Is 36 or 38 ATP Produced in Cellular Respiration?
The net ATP production in cellular respiration varies between 36 and 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. This discrepancy arises due to minor differences in how energy is shuttled during the process. The breakdown is generally as follows:- Glycolysis: 2 ATP
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP
- Electron Transport Chain: 32-34 ATP
What Are the Outputs of Cellular Respiration?
The outputs are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. These molecules are essential not only as waste (carbon dioxide and water) but as sources of cellular energy (ATP).What Are the Reactants of Cellular Respiration?
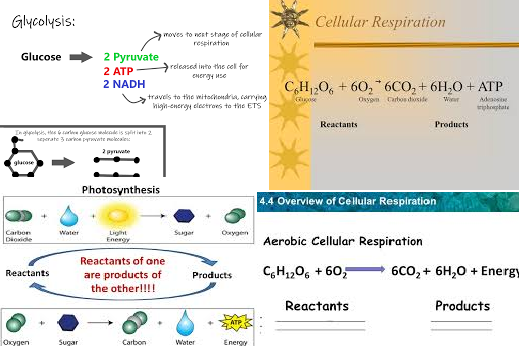
The reactants for cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen. The overall process can be represented by the formula: C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+ATP\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{O}_2 \rightarrow 6\text{CO}_2 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{ATP}Is Oxygen a Product or Reactant?
Oxygen is a reactant in cellular respiration. It acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, making it essential for ATP production and water formation.What Is the Final Product of ATP?
ATP itself is a high-energy molecule used immediately by the cell. After ATP releases energy, it transforms into ADP (adenosine diphosphate), which can later be recharged back into ATP through cellular respiration.What Is the Main Source of Energy for Cellular Respiration?
The main energy source for cellular respiration is glucose, a carbohydrate obtained from food. Cells break down glucose to release energy, which is then stored in ATP.What Is the Formula for Cellular Respiration?
The simplified formula for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+ATP\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{O}_2 \rightarrow 6\text{CO}_2 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{ATP} This equation highlights glucose and oxygen as the primary reactants and carbon dioxide, water, and ATP as the main products.What Is Produced by Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide, water, and ATP as its main products. These are essential for various cellular activities and maintaining the body’s overall energy levels.Who Discovered Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration was first described in detail by Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century. He connected respiration to the oxidation of nutrients, pioneering the concept of cellular energy transformation.Which Form of Energy Is Stored in Glucose?
Glucose stores chemical energy in its molecular bonds. When broken down in cellular respiration, this chemical energy is converted into ATP, which cells can directly use for energy. Cellular respiration is a critical process for life, powering every action from muscle movement to cellular repair. By breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen, it produces the necessary ATP, carbon dioxide, and water, driving all energy-dependent functions in living organisms.Read more :
1= https://checkwebsitedr.com/blogs/what-are-the-products-of-cellular-respiration/
2= https://checkwebsitedr.com/blogs/what-is-called-a-president/