Website owners and webmasters often use a 301 redirect to permanently send website visitors to a new URL. A 301 redirect indicates to search engines and browsers that a page has moved permanently, ensuring that users and link equity are redirected to the new URL.
For example, if your company changes its name from ABCShoes to XYZShoes, you want visitors who type in ABCShoes.com to automatically be redirected to XYZShoes.com. This helps retain previous customers and maintain your website’s ranking and SEO value.
While a 301 redirect is essential for permanent URL changes, it may not always be the best option for every scenario. Understanding its impact on SEO, along with best practices, is critical for optimizing your website performance.
How 301 Redirects Affect Website Rankings
1. Passing Link Equity
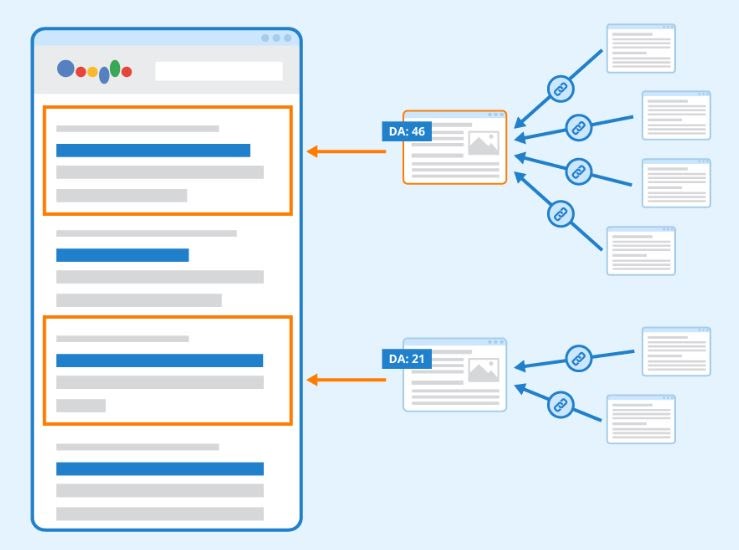
One of the main benefits of a 301 redirect is that it passes most (if not all) of the link equity (or "link juice") from the old URL to the new one. This ensures that your new URL retains the SEO value from backlinks pointing to the original URL. Google and other search engines recognize the redirect and apply the original page's ranking signals to the new page, minimizing any negative impact on rankings. However, improper or overuse of 301 redirects can lead to rank loss, as search engines may struggle to follow complex redirect chains or may fail to properly pass the link equity. Therefore, it’s crucial to use 301 redirects sparingly and with purpose.2. Permanent Changes to Google Indexing
A 301 redirect tells search engines that the old URL is no longer valid and that the new URL should be indexed in its place. Once the redirect is in place, Google will de-index the old page and replace it with the new URL. If you’re not fully prepared for this permanent change, your website could lose ranking and visibility. This is particularly concerning for temporary campaigns where the old URL may need to be reused in the future. In such cases, a 302 redirect (temporary redirect) would be a better choice to retain SEO benefits on the original URL.3. Potential for Page Speed Issues
Although a 301 redirect itself is relatively fast, multiple redirects or long redirect chains can slow down page load times. Since page speed is a critical ranking factor in Google's algorithm, poorly managed redirects can harm your SEO. To avoid this, ensure that 301 redirects are implemented efficiently. Eliminate unnecessary redirects and reduce redirect chains that can slow down the user experience.4. Impact on User Experience
301 redirects ensure that users trying to visit your old URL seamlessly arrive at the new page. This maintains user experience and prevents broken links, which could negatively affect your SEO and reputation. However, it's important to update internal links to reflect the new URL rather than relying on 301 redirects for every link.5. Risk of Losing Traffic
In certain scenarios, using a 301 redirect can lead to a loss in traffic. For example, if a page that ranks for a set of specific keywords is redirected to a page with entirely different content, you risk losing organic traffic. The new page may not rank as highly for the old page’s keywords, leading to a drop in visibility.Best Practices for Using 301 Redirects
1. Ensure Relevance Between Old and New URLs
When setting up a 301 redirect, it’s essential to ensure that the new page is relevant to the old one. This means the content should be similar and serve the same user intent. This will help maintain your rankings and traffic, as Google expects the redirect to lead to a page that fulfills the same purpose.2. Avoid Redirect Chains and Loops
A redirect chain happens when one URL redirects to another, and then that URL redirects to yet another URL. This can slow down your site and cause confusion for search engines, which may result in lost rankings. Similarly, redirect loops (where two URLs continuously redirect to each other) can severely harm your SEO and user experience. Ensure that you set up direct 301 redirects from the old URL to the new one, without any intermediate steps.3. Update Internal Links
After implementing a 301 redirect, you should update your internal links to point directly to the new URL. This helps reduce the load on your server and ensures that users and search engines are always directed to the correct page without unnecessary redirects.4. Monitor Performance
It’s essential to monitor the performance of pages that have 301 redirects. Use tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics to track any changes in rankings, traffic, and user behavior. If you notice a significant drop in traffic, you may need to review your redirect strategy.5. Don’t Use 301 Redirects for Temporary Changes
If your redirect is only needed for a short period (for instance, during site maintenance or a limited-time campaign), use a 302 redirect instead of a 301. A 302 tells search engines that the redirect is temporary, and it ensures that the old URL retains its ranking power and indexing.301 Redirect Issues and How to Fix Them By Ahrefs
1. HTTP Pages Still in Use
Issue: Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is crucial for site security and rankings, as Google recognizes HTTPS as a ranking signal. However, after migration, some pages may still be accessible via HTTP if the redirect isn't applied correctly. How to Fix:- Step 1: Use Ahrefs' Site Audit to crawl your website and check the Internal Pages report for any remaining HTTP URLs.
- Step 2: Ensure all HTTP pages are redirected to their HTTPS counterparts using a 301 redirect.
- Step 3: Verify the redirects are working across all pages, ensuring visitors are only seeing the HTTPS version of your website.
2. Redirect Chains
Issue: Redirect chains occur when there are multiple redirects between the original URL and the final destination. While Google can follow these chains, they can slow down site performance and negatively impact user experience. How to Fix:- Step 1: Use Ahrefs' Site Audit to identify any URLs involved in redirect chains.
- Step 2: Replace intermediate redirects with a direct 301 redirect to the final destination page.
- Best Practice: Keep the number of redirects in a chain to a minimum—ideally no more than three.
3. Broken Redirects
Issue: A broken redirect sends users or search engines to a page that no longer exists, returning a 404 status code. This harms SEO as both users and search engines are unable to access the content. How to Fix:- Step 1: Use the Internal Pages report in Ahrefs' Site Audit to find any broken redirects (404 errors).
- Step 2: Fix these errors by either:
- Removing links that point to the dead or redirected URL.
- Restoring the destination page if it was removed unintentionally.
4. 301 Redirects in a Sitemap
Issue: Sitemaps should only contain canonical and indexable pages. Including 301 redirects in the sitemap wastes crawl budget because search engines will continue to crawl URLs that are no longer relevant. How to Fix:- Method 1: Manually check your sitemap by visiting
domain.com/sitemap_index.xmlordomain.com/sitemap.xml, then use an HTTP status code checker to find 301 redirects. - Method 2: Use Ahrefs' Site Audit to crawl your site and look for “3XX redirect in sitemap” errors.
- Step 3: Remove any 301-redirected URLs from your sitemap and replace them with the canonical URL.
5. External Redirecting Links
Issue: Sometimes, the external websites you link to may implement a 301 redirect to a new page. If this new page is irrelevant or harmful, it can negatively affect your site’s SEO and credibility. How to Fix:- Step 1: Use Ahrefs' Site Audit to find external links that now point to 301-redirected pages.
- Step 2: Review these links and ensure the new destination page is relevant and trustworthy.
- Step 3: Manually update or remove the link if the destination is irrelevant or harmful.