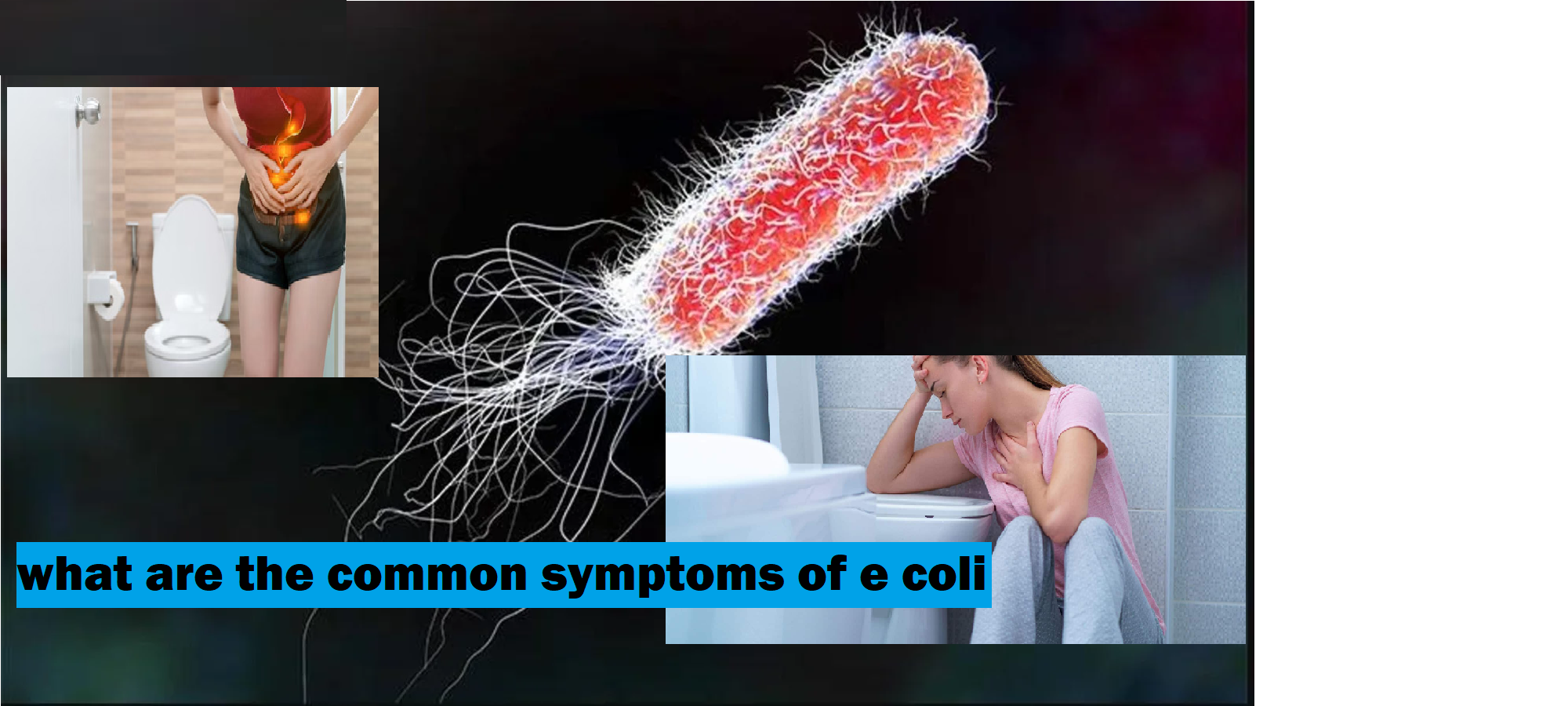
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a type of bacteria that can cause various health issues, particularly gastrointestinal infections. Understanding the common symptoms and causes of E. coli infections is crucial for prevention and treatment. This article will cover the symptoms of E. coli, its common causes, and essential information for managing an infection.
Common Symptoms of E. coli
The symptoms of E. coli infections can vary depending on the strain and the individual, but the following are the most common signs:- Abdominal Cramps: Many individuals experience severe abdominal cramps, which can be painful and uncomfortable.
- Diarrhea: This symptom often starts as watery diarrhea but can become bloody in more severe cases.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may accompany diarrhea, leading to dehydration if fluids are not replaced.
- Fever: Some strains of E. coli can cause mild fever, although it is not always present.
- Fatigue: Many patients report feeling tired and weak, which can be a result of dehydration and the body’s immune response to infection.
Three Common Causes of E. coli
E. coli infections can occur due to various factors, including:- Contaminated Food: Undercooked ground beef, raw vegetables, unpasteurized dairy products, and contaminated water are common sources.
- Person-to-Person Transmission: E. coli can spread through close contact with an infected person, especially in settings like daycare centers.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Not washing hands properly after using the bathroom or before handling food can contribute to the spread of E. coli.
Symptoms of High E. coli Levels
High levels of E. coli in the body may lead to severe symptoms, including:- Severe abdominal pain
- Prolonged diarrhea, potentially bloody
- Signs of dehydration (dry mouth, dizziness, decreased urination)
- Fever
Common Diseases Caused by E. coli
E. coli is associated with several diseases, including:- Gastroenteritis: Inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): E. coli is one of the most common causes of UTIs.
- Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS): A serious complication that can result from certain E. coli strains, leading to kidney failure.
- Bacteremia: A bloodstream infection that can occur in severe cases.
- Meningitis: Rarely, E. coli can cause infections in the brain or spinal cord.
Best Treatment for E. coli
The primary treatment for E. coli infections is supportive care, which includes:- Hydration: Ensuring adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
- Rest: Giving the body time to recover.
- Avoiding Anti-Diarrheal Medications: These can prolong the infection in some cases.
Antibiotics and E. coli
Generally, antibiotics are not recommended for E. coli infections, particularly for those caused by Shiga toxin-producing strains, as they can increase the risk of complications like HUS.Foods Causing E. coli
E. coli outbreaks are often linked to:- Undercooked beef
- Raw leafy greens
- Unpasteurized milk and juices
- Contaminated water sources
How E. coli Affects the Body
E. coli primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms of diarrhea and abdominal cramps. In severe cases, toxins released by certain strains can enter the bloodstream and damage organs, particularly the kidneys.At-Risk Populations
Certain groups are at higher risk for severe E. coli infections, including:- Young children
- Elderly individuals
- People with weakened immune systems
Confirming E. coli Infection
To confirm an E. coli infection, healthcare providers typically perform stool tests to identify the presence of the bacteria.Duration of Symptoms
Symptoms of E. coli infections usually last from 3 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health.How to Avoid E. coli
To minimize the risk of E. coli infections, follow these precautions:- Cook meat thoroughly: Ground beef should reach an internal temperature of 160°F (70°C).
- Wash hands: Always wash hands with soap after using the bathroom and before preparing food.
- Avoid cross-contamination: Use separate cutting boards for raw meat and other foods.
- Wash fruits and vegetables: Rinse all produce under running water before eating.
Conclusion
Understanding what are the common symptoms of E. coli is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By being aware of the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and ensure better health outcomes. If you suspect an E. coli infection, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper guidance and care.Read more :
1= https://checkwebsitedr.com/blogs/what-size-is-a-king-bed-and-a-queen-bed/
2= https://checkwebsitedr.com/blogs/what-are-the-common-symptoms-of-e-coli/
3= https://checkwebsitedr.com/blogs/what-are-the-causes-of-parkinsons-disease/